What is EXPANDABLE POLYSTYRENE (EPS) ?
Styropor is a brand name of BASF AG. The Company began with manufacture of expanded polystyrene (popularly known as Styrofoam)- a BASF AG invention.
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a rigid cellular plastic that is made from expandable polystyrene that contains an expansion agent. It is most commonly used for packaging foodstuffs, medical supplies, electrical consumer goods and insulation panels for building.
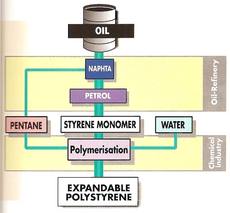
What is Expandable Polystyrene made from?
Polystyrene is extracted from oil. Thousands of small units of styrene, called monomers, link together to form large molecules of polystyrene by a process called polymerization.
The Expandable Polystyrene (EPS) production process uses a pure hydrocarbon, which does not contain any halogens and does not damage the earth's protective ozone layer, as the expansion agent.
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a rigid cellular plastic that is made from expandable polystyrene that contains an expansion agent. It is most commonly used for packaging foodstuffs, medical supplies, electrical consumer goods and insulation panels for building.
What is Expandable Polystyrene made from?
Polystyrene is extracted from oil. Thousands of small units of styrene, called monomers, link together to form large molecules of polystyrene by a process called polymerization.
The Expandable Polystyrene (EPS) production process uses a pure hydrocarbon, which does not contain any halogens and does not damage the earth's protective ozone layer, as the expansion agent.
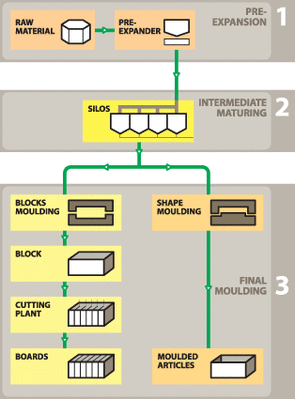
How is EXPANDABLE POLYSTYRENE (EPS) processed?
The process involved in making EXPANDABLE POLYSTYRENE (EPS) is quite easy to explain. Expanded polystyrene starts as small spherical beads with a typical diameter of 0.5-1.5mm. They contain an expanding agent. When the beads are heated with steam, the agent starts to boil, the polymer softens and the beads expand to about forty times their initial size.
After a maturing period to equilateral temperature and pressure, the pre-foamed beads, which now have a closed cellular foam structure, are packed in a mold and again reheated with steam.
The mold is made in the same shape as the finished article. The pre-foamed beads expand further, completely fill the mold cavity and fuse together. When molded, nearly all the volume of the EXPANDABLE POLYSTYRENE (EPS) foam (in fact 98%) is air. This is what makes EXPANDABLE POLYSTYRENE (EPS) so lightweight and buoyant.
The process involved in making EXPANDABLE POLYSTYRENE (EPS) is quite easy to explain. Expanded polystyrene starts as small spherical beads with a typical diameter of 0.5-1.5mm. They contain an expanding agent. When the beads are heated with steam, the agent starts to boil, the polymer softens and the beads expand to about forty times their initial size.
After a maturing period to equilateral temperature and pressure, the pre-foamed beads, which now have a closed cellular foam structure, are packed in a mold and again reheated with steam.
The mold is made in the same shape as the finished article. The pre-foamed beads expand further, completely fill the mold cavity and fuse together. When molded, nearly all the volume of the EXPANDABLE POLYSTYRENE (EPS) foam (in fact 98%) is air. This is what makes EXPANDABLE POLYSTYRENE (EPS) so lightweight and buoyant.
